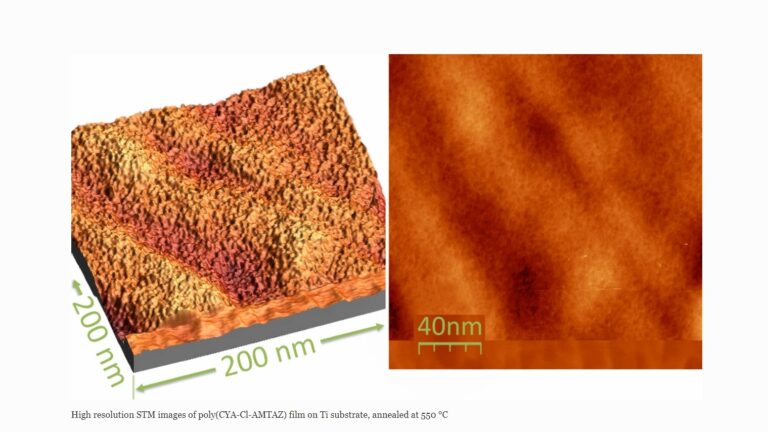
Result description
In the present invention, uniform flexible carbon nitride coatings are produced in a manner very similar to that usually employed for fabrication of the so called glassy, or turbostratic carbon – by thermal transformation of crosslinked polymeric resins. The coatings exhibit fascinating electrochemical stability and drastically increase the capacitance of coated carbon cloth electrodes. Annealed films exhibit extrinsic semiconducting behavior with optical bandgaps in the range from 1.71 to 1.99 eV and fairly good conductivity. The outstanding long-term electrochemical stability of annealed films makes them competitive with pyrolytic carbon, while much lower annealing temperatures allow preparation of nanocomposites with various particles. The precursor polymers were obtained by self-condensation of 2-amino-4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazine and condensation of cyanuric chloride with 5-aminotetrazole and 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole-5-carboxylic acid, respectively, in N,N-dimethylacetamide. The polymers contain mainly C-N skeletal bonds and can therefore be viewed as “extension” of typical carbon nitride precursors, like melamine, to polymeric structure.
Addressing target audiences and expressing needs
- Grants and Subsidies
- Incubators / Accelerators
- I/we wish to transfer my/our IPR to an interested party
I’m currently looking for a fellowship program to put into practice the results that have been patented. I already have a project and a receiving institution (EURECAT Tarragona, Spain).
- Public or private funding institutions
- Other Actors who can help us fulfil our market potential
- Private Investors
R&D, Technology and Innovation aspects
The materials synthesised and protected by the patent are the only conductive “electrochemical glue” known at the moment. They allow to fix nanoparticles on electrodes surfaces, facilitation creation of fuel cells, censors, electrolysers and many other types of electrochemical devices.
The possible business model in the case of the presented invention includes synthesis of the polymeric precursors and on-demand fabrication of electrodes. The precursors can be viewed as a product per se and sold to companies, fabricating electrodes for water electrolysis, fuel cells, censors, etc. This business model can be scaled according to the model of selling a chemical product with various potential uses, well-elaborated in the chemical industry. Fabrication of electrodes is a different model, which can be scaled by research efforts with increase of the number of possible implementations of precursors and coatings. At the moment, two potential markets for electrode production are scientifically confirmed: oxygen evolution electrodes for electrolysis and formic acid oxidation electrodes for fuel cells, although much more potential applications are possible.
All results, described in the patents and in the articles, have been replicated several times. Both synthesis of the precursors and electrodes fabrication are stable processes, resulting in reproducible quality of their products.
This technology is highly sustainable in comparison with competitive technologies mainly due to non-utilization of precious and critical materials. In all currently implemented industrial cases, precious metals (Pt, Ir, Ru and others) or critical materials (Ce) are used. The current invention allows to fabricate electrodes with similar properties on the basis of abundant elements: C, N, P, Ni
Result submitted to Horizon Results Platform by UNIVERSITAT ROVIRA I VIRGILI