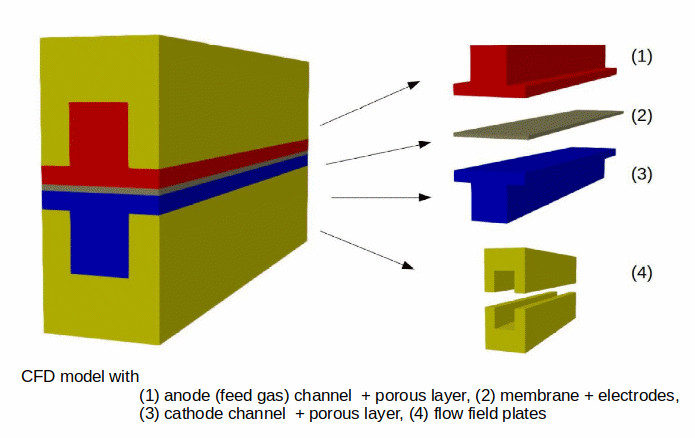
Result description
Water management is a key issue for hydrogen separation and compression cells. The presented model allows to capture the two general effects of electro osmotic drag and water back diffusion through the membrane. The temperature difference within the cell remained smaller than 2 K throughout all simulations. The following conclusions are derived.
1. Overall, the current density distribution is very homogeneous. The distribution of hydrogen throughout the flow field should not be a problem.
2. The effect of electro osmotic drag requires the humidification of the inlet gas stream. A high water content would be achieved by an operating temperature which is significantly greater than room temperature.
3. The effect of water back diffusion leads to an internal ‘recycling’ of the water from the cathode side. Since the driving force is a difference in saturation, this effect can never fully compensate the osmotic drag.
Addressing target audiences and expressing needs
- Business partners – SMEs, Entrepreneurs, Large Corporations
- Collaboration
Developers of fuel cells, electrolyzers and electrochemical hydrogen compression and separation
- Other Actors who can help us fulfil our market potential
- Research and Technology Organisations
- Academia/ Universities
Result submitted to Horizon Results Platform by FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH